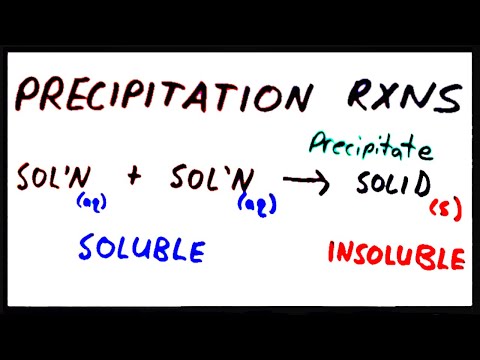
Alright, so in this video, I'm going to go over precipitation reactions. In my last video, I was talking about the solubility of ionic compounds and the rules for determining whether an ionic compound is soluble or insoluble. These rules are going to come in handy when we do precipitation reactions. In general, what we do in precipitation reactions is mix two or more solutions together. These solutions can be ions or soluble ionic compounds. Upon mixing these solutions, a solid forms out of the solution. This solid is called a precipitate. The word precipitate can be used as a noun or verb. The solutions that we start with are always going to be soluble ionic compounds. We express the fact that they're soluble by attaching aq in parentheses at the very end. These parentheses are very important when doing precipitation reactions, and you can't leave them out. For a soluble ionic compound, you're going to use "aq" for aqueous. Both of these are soluble ionic compounds. However, if the product of the reaction is an insoluble ionic compound, then you would use "s" in parentheses for solid. Otherwise, if it was soluble, you would use "aqueous" just like the reactants. Let's go through an example of precipitation reactions. Suppose I have silver ion (Ag+) and that is aqueous, and chloride ion (Cl-) that is also aqueous. Suppose I have a solution of silver ion and a solution of chloride ion, and they're both dissolved. Now upon mixing these two solutions together, the formula for the product is going to be AgCl. Now we have to assign the state of matter that AgCl is in. Is it solid or aqueous? That's where the solubility rules are going to come in handy. Let's look at the solubility rules for this compound and see if we...
Award-winning PDF software





Video instructions and help with filling out and completing Will Form 8865 Thereof